Vestibular Rehabilitation
What is Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Vestibular rehabilitation is a specifically designed series of exercise programs to help improve balance or dizziness related problems caused by inner ear conditions. Each bespoke program is designed by a Physiotherapist specialised in vestibular disorders.
Anyone who has been diagnosed with, or experiences dizziness, vertigo, imbalance, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, neck movement dizziness, Meniere’s Syndrome or suffer from regular headaches or migraines may benefit from starting a vestibular rehabilitation program.
Vestibular rehabilitation can also be beneficial for anyone who has suffered from brain injury or experiences regular falls.
What to Expect from Vestibular Rehabilitation
Our specially trained Physiotherapists will perform a thorough evaluation through a series of tests and questions. The results are explained in detail to the patient and any questions or concerns will be addressed at the same time.
The Physiotherapist will then design an individualised exercise plan along with the recommended frequency of treatment sessions.
The treatment plan will include exercises to strengthen posture, gait and components of the balance system, such as eyes, ears and legs. During the treatment process, a home exercise program will be designed and implemented specific to the tolerance, physical condition and diagnosis of each patient.
How can Vestibular Rehabilitation help?
Most imbalance conditions can be helped through vestibular rehabilitation. The goal of treatment is to minimize dizziness, improve balance and prevent falls by restoring normal function of the vestibular system by retraining through specific exercise programs.
These exercises are designed to retrain the brain to recognize and process signals from the vestibular system, therefore desensitizing the patient to movements that provoke symptoms.
The ultimate goal of vestibular rehabilitation is to restore normal every day function. Other expected outcomes after vestibular rehabilitation are as follows:
- Decrease in dizzy episodes
- Reduction of falls
- Improved balance and motion control
- Improve ability to stabilize stair or gaze
- Less headaches or migraines
What Causes Vestibular Disorders?
Many people experience equilibrium disorders at some point in their lives and feel that the loss of balance or unsteadiness is a result of natural ageing. They are often surprised to learn that the source of the problem may be the inner ear.
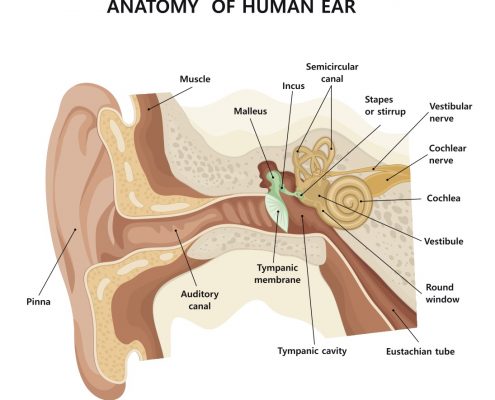
The vestibular system includes parts of the inner ear and is the primary organ of human equilibrium. Human equilibrium (balance) is a complex interaction requiring proper input from the vestibular, vision and somatosensory systems.
If the vestibular system becomes affected by illness, infections, mechanical changes or head trauma the brain will receive altered signals as an exaggeration of motion that can result in what we experience as dizziness or vertigo.
What are the Symptoms of Vestibular Disorders?
- Vertigo and dizziness
- Imbalance, spatial disorientation (or need to hold on to an object when walking)
- Visual disturbances
- Headaches or migraines
- Hearing Changes
- Cognitive and/or psychological changes
- Frequent falls
- The sensation of “foggy” head or wooziness
How Long Does it Take to Recover from Vestibular Disorders?
This is the most common question asked by our patients and a difficult one to answer. This is because there are so many causes for vestibular symptoms like dizziness or loss of balance. Generally, one or two treatments per week for 6-8 weeks will show a good improvement. Some patients respond quicker, others may take longer.
Once you have had an initial assessment and first treatment, your Physiotherapist will be able to provide you with a better indication of how long it will take to regain normal function as well as the likely outcomes.
What Type of Exercises are uses with Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Exercise plans and progressions are individually constructed appropriate to the diagnosis and requirements of each patient. The speed of improvement can vary from person to person therefore creating a flexible program is also important.
Here is a list of the key areas for which exercises are produced:
- Balance retraining
- Vision stability exercises
- Stable walking exercises
- Postural training
- Neck mobility
- Manual therapy
- General fitness
- Workplace training – through either a workplace or workstation assessment, adjustments and advice can be provided to ensure correct posture is adopted and hardware eg computer screens and desks, are appropriately positioned. Follow this link to our Occupational Health page.
Call Us Now 012 3456789
Or Send Your Request Below